Instantaneous Velocity and Speed
Instantaneous Velocity and Speed: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Average Velocity,Average Velocity when Time Intervals Given,Average Velocity when Distance Travelled Given, etc.
Important Questions on Instantaneous Velocity and Speed
A particle goes from to with a speed of and to with a speed of . If , the average speed in between and is
A car moves a distance of 200 m. It covers the first half of the distance at speed and the second half of distance at speed v. The average speed is . Find the value of v
A bus travelling the first one third distance at a speed of , the next one third at and the last one – third at . The average speed of the bus is
A particle covers half of its total distance with speed and the rest half distance with speed . Its average speed during the complete journey is
A car covers the first half of the distance between two places at and other half at . The average speed of the car is
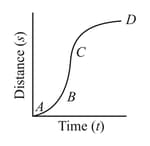
A particle shows distance–time curve as given in this figure. The maximum instantaneous velocity of the particle is around the point:
A car moves from X to Y with a uniform speed and returns to X with a uniform speed . The average speed for this round trip is
A particle moves along a straight line such that its displacement at any time t is given by
metres
The velocity when the acceleration is zero is
The displacement of particle moving in one dimension, under the action of a constant force is related to the time by the equation where is in meters and in seconds. Find the displacement of the particle when its velocity is zero.
The coordinates of a moving particles at any time are given by and . The speed of the particle at time is given by –
The coordinates of a moving particles at any time are given by and . The speed of the particle at time is given by –
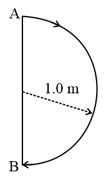
In , a particle goes from point to point , moving in a semicircle of radius (see figure). The magnitude of the average velocity is
A vehicle travels half the distance with speed and the remaining distance with speed . Its average speed is:
The distance travelled by an object in time is given by . The instantaneous speed of the object at will be :
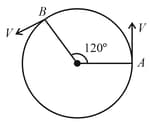
As shown in the figure, a particle is moving with constant speed . Considering its motion from to , the magnitude of the average velocity is:
A person travels distance with velocity and then distance with velocity in the same direction. The average velocity of the person is , then the relation between and will be
If position of particle is changing with time as . Find the velocity at
An object moves distance with speed and next distance with speed . The average velocity is related to and as
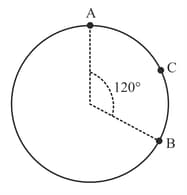
A particle moves from A to B via C with uniform speed . Average velocity during the journey is equal to
The path of a particle is given by the expression , where and are constants. is the displacement at time . Find its velocity at any instant.
